Linux Task Management
Process, Thread and Task
| Managing unit | Description |
|---|---|
| Task | Resource acquisition unit |
| Thread | Running unit |
| Process | Running or runnable program |
| Program | Executable file stored in disk |
-
Executable file is compiled to be a set of binary machine instructions and data
-
Program and Process
$ gcc -o test test.c
$ file test
test: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object, x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked, interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0, BuildID[sha1]=c1919678864f40218323926252afd86ca1cc01dc, with debug_info, not stripped
$ ls test # Program
test
$ ps
PID TTY TIME CMD
814 pts/3 00:00:00 bash
6507 pts/3 00:00:00 test # Process
6508 pts/3 00:00:00 ps
- Scheduling is determining processes to acquire CPU resource by the Kernel.
Process structure
- Virtual address space structure
- One of the representative resource being allocated by the kernel to run process
CPU Virtual memory allocation User space Kernel space 32bit 4 GB 2^(2+10+10+10) 0 ~ 3 GB 3 ~ 4 GB 64bit 16 EB (Exa = 1024^6) 0 ~ 128 TB 128 TB ~ 16 EB 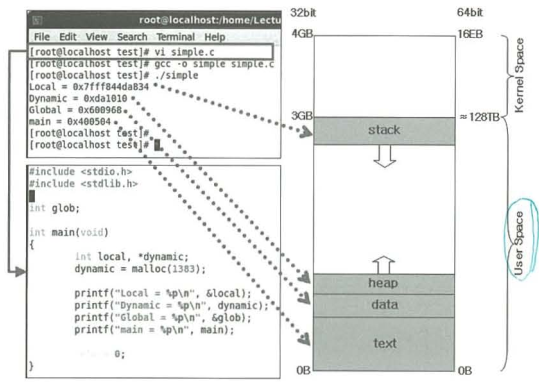
Segment (Virtual Memory Area Structure) Location Contents Stack region Growing down from 3GB(32bit) or 128TB(64bit) Local variables and arguments for functions Heap region Growing up from the top of Data region Dynamically allocated memory with malloc() / new() Data region Fixed region on top of Text region Global variables Text region Fixed region at the beginning of user space CPU instructions
Creation and Execution of Process and Thread
-
fork()
#include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int global_cnt = 2; int main(void) { pid_t pid; int local_cnt = 3; printf("PID(%d): Parent global_cnt=%d, local_cnt=%d \n", getpid(), global_cnt, local_cnt); if (pid = fork() < 0) { perror("fork error"); exit(1); } else if (pid == 0) { global_cnt++ local_cnt++ } else { wait(); } printf("PID(%d): global_cnt=%d, local_cnt=%d \n", getpid(), global_cnt, local_cnt); return 0; }$ gcc -o fork fork.c $ ./fork PID(10404): Parent global_cnt=2, local_cnt=3 PID(10405): global_cnt=3, local_cnt=4 PID(10404): global_cnt=2, local_cnt=3 -
clone()
// #include <sys/types.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sched.h> int global_cnt = 2; int sub_func(void *arg) { global_cnt++; printf("PID(%d): Child global_cnt=%d \n", getpid(), global_cnt); sleep(2); return 0; } int main(void) { pid_t pid; int child_stack[4096]; int local_cnt = 3; printf("PID(%d): Parent global_cnt=%d, local_cnt=%d \n", getpid(), global_cnt, local_cnt); clone(sub_func, (void *)(child_stack+4095), CLONE_VM | CLONE_THREAD | CLONE_SIGHAND, NULL); sleep(1); printf("PID(%d): Parent global_cnt=%d, local_cnt=%d \n", getpid(), global_cnt, local_cnt); return 0; }$ gcc -o clone clone.c $ ./clone PID(17351): Parent global_cnt=2, local_cnt=3 PID(17351): Child global_cnt=3 PID(17351): Parent global_cnt=3, local_cnt=3Forked Process Cloned Thread Virtual memory address space Create another Share the same Resource cost Doubled Minimized Error propagation Parent is not affected Parent can be affected -
execl()
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void)
{
pid_t pid;
int exit_status;
if (pid = fork() < 0) {
perror("fork error");
exit(1);
}
else if (pid == 0) {
printf("Before execl() \n");
execl("./fork", "fork", (char *)0);
printf("After execl() \n");
}
else {
pid = wait(&exit_status);
}
printf("Parent \n");
return 0;
}
$ gcc -o fork_exec fork_exec.c
$ ./fork_exec
Before execl()
PID(17453): Parent global_cnt=2, local_cnt=3
PID(17454): global_cnt=3, local_cnt=4
PID(17453): global_cnt=2, local_cnt=3
Parent
- After execl() is not printed because “execl()” replace the process image “fork_exec” (including text, data, stack) with the previous image “fork”.
- In this case, “vfork()” can be used for the same address space with parent’s so that redundant memory space does not created before being replaced with the previous image “fork”.
 Cool Wind on Study
Cool Wind on Study