Interupt, Trap and System Call
Interupt Handling Procedure
System Call Handling Procedure
Additional System Call Implementation
- Adding a new system call
- Add a new system call number “317” and register the signature “sys_newsyscall()” to the “sys_call_table” in the “~/arch/x86/kernel/syscalls/syscall_64_tbl” file.

- Add the new system call declaration in the “~/include/linux/syscall.h”.
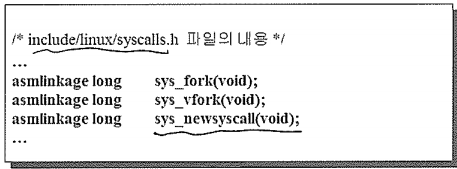
- Add the new system call definition in the “kernel/” or “fs/”(for file system related system call).
#include <linux/unistd.h> #include <linux/errno.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/sched.h> asmlinkage long sys_newsyscall(void) { printk("<0>Hello Linux, I'm in Kernel! \n"); return 0; } EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(sys_newsyscall);- Conventional prefix “sys_”
- Return value is “long”
- Keyword “asmlinkage”
- Do nothing with Intel CPU
- Several preprocessing with Alpha CPU
- Kernel print function “printk”
- Add the object file name in the “kernel/Makefile” to be compiled together

- Implement an user application using the added system call
- Without using a library
- With using a library
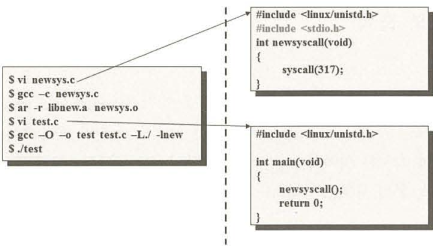
- Make the library with "ar" command - Use gcc option "-l" for linking the library - Use gcc option "-L" for specifying the directory includes the library
System Call Implementation Extended
- Two major objectives for using system call
- Ask kernel to execute a kernel service
- Ask kernel to offer kernel information to an user application
- “getpid()”, “stat()”, etc.
- Kernel information output
- “current” is the pointer to the “task_struct” of the running task.
asmlinkage long sys_gettaskinfo(void) { printk("<0> PID: %d \n", current->pid); printk("<0> TGID: %d \n", current->tgid); printk("<0> PPID: %d \n", current->parent->pid); printk("<0> STATE: %d \n", current->state); printk("<0> PRIORITY: %d \n", current->prio); printk("<0> POLICY: %d \n", current->policy); printk("<0> Number of MAJOR FAULT: %d \n", current->maj_flt); printk("<0> Number of MINOR FAULT: %d \n", current->min_flt); return 0; }- Argument passing#include <linux/unistd.h> #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <asm/uaccess.h> asmlinkage int sys_show_mult(int x, int y, int* res) { int error, compute; int i; error = access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, res, sizeof(*res)); if (error < 0) { printk("error in cdang \n"); printk("error is %d \n", error); return error; } compute = x*y; printk("compute is %d \n", compute); i = copy_to_user(res, &compute, sizeof(int)); // include/asm/uaccess.h return 0; }#include <stdio.h> #include <linux/unistd.h> int main(void) { int mult_ret = 0; int x = 2, y = 5; int i; i = syscall(318, x, y, &mult_ret); printf("x is %d \n", x); printf("y is %d \n", y); printf("ret is %d \n", mult_ret); return 0; }
- Argument passing using struct
- Maximum size of arguments for system call
- 32 bit or 64 bit
- Maximum number of arguments for system call
- 6 for Intel CPU
// mystat.h #include <linux/kernel.h> #include <linux/sched.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <linux/uaccess.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/fdtable.h> struct mystat { pid_t pid; pid_t ppid; int stat; int priority; int policy; long utime; long stime; long starttime; unsigned long min_flt; unsigned long maj_flt; long open_files; }#include "mystat.h" asmlinkage int sys_gettaskinfo(int id, struct mystat* user_buf) { struct mystat* buf; int i, cnt = 0; struct task_struct *search; struct file *fp; // pid_task() or get_pid_task() to get a pointer to the struct task_struct of the process. // If the call returns NULL then the process does not exist. // pid_task() searches task with specified PID, sequentially from the init_task search = pid_task(id, PIDTYPE_PID); if(search == NULL) return -1; buf = (char*)kmalloc(sizeof(struct mystat), GFP_KERNEL); if(buf == NULL) { printk("buf is NULL \n"); return -1; } buf->pid = search->pid; buf->ppid = search->parent->pid; buf->stat = search->state; buf->priority = search->prio; buf->policy = search->policy; buf->utime = search->utime; buf->stime = search->stime; buf->starttime = search->start_time.tv_sec; buf->min_flt = search->min_flt; buf->maj_flt = search->maj_flt; for (i = 0; i<32; i++) { if ((search->files->fd_array[i]) != NULL) { cnt++; } } buf->open_files = cnt; copy_to_user(user_buf, buf, sizeof(struct mystat)); return 0; }#include "mystat.h" #include <linux/unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int task_number; struct mystat* mybuf; if (argc != 2) { printf("Usage: a.out pid \n"); exit(1); } task_number = atoi(argv[1]); mybuf = (char*)malloc(sizeof(struct mystat)); if (mybuf == NULL) exit(1); syscall(319, task_number, mybuf); printf("pid is %d \n", (int)mybuf->pid); printf("ppid is %d \n", (int)mybuf->ppid); printf("state is %d \n", (int)mybuf->stat); printf("Policy is %d \n", (int)mybuf->policy); printf("File count is %d \n", (int)mybuf->open_files); printf("Start time is %d \n", (int)mybuf->starttime); return 0; } - Maximum size of arguments for system call
 Cool Wind on Study
Cool Wind on Study