Linux File System and Virtual File System
File System
- Main Memory vs. Secondary Storage
| Memory | Memory Management | Device | Volatility | Accessing Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| main memory | virtual memory | RAM | volatile | page frame |
| secondary storage | file system | hard disk | non-volatile | disk block + FILE NAME |
Disk Block Management
-
Disk
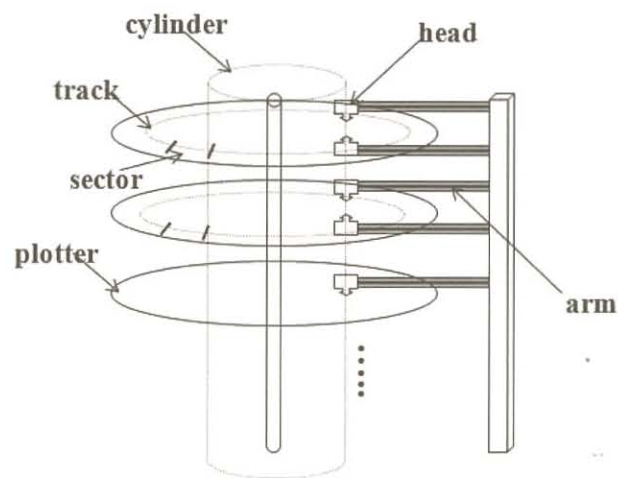
- Plotter
- Track
- Sector: base unit for read and write on a disk
- Cylinder: a set of Tracks at the same position through different plotters
- Track
- Arm
- Head
- Plotter
- Data Access Time
- Seek time: head traveling time to the desired track
- Rotational latency: plotter spinning time to reach the desired sector by a head
- Transmission time: reading or writing time by a head
- Disk Block
- Generally, its size is the same as page frame’s one.
- Regular page fram size: 4 KB
- Larger disk block, faster disk I/O.
- Larger disk block, less efficient memory usage.
- Generally, its size is the same as page frame’s one.
- Disk Block - Sectors
- Block device driver (“read_ahead” variable)
- Disk block numbers can be mapped to the corresspondent sectors
- It is done by
- Disk device driver or
- Disk controller
- It is done by
- Two ways of disk block allocation
- Sequential allocation
- Being hardly ever seen…
-
Non-sequential allocation
Method Pros Cons Block chain no index block lose one block, lose the next whole data Index block direct access by indexing 1) lose the index block, lose the whole data. 2) limited index block size FAT unique FAT(index block) for a whole file system lose the FAT, lose the whole data - Block chain
- Index block
- FAT
- Sequential allocation
FAT
inode structure
-
ext2_inode
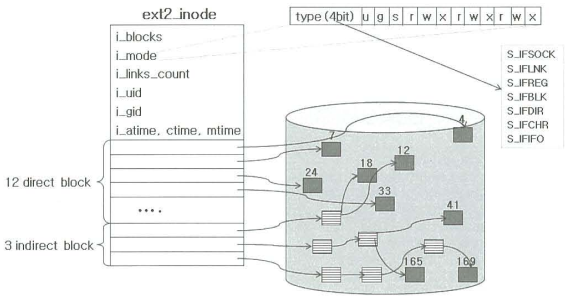
Field Description i_blocks number of data blocks i_mode file format and access rights i_size file length in bytes i_links_count number of files indicating the inode i_uid, i_gid user ID, group ID i_atime, i_ctime, i_mtime accessed time, created time, modified time i_flags flie flags osd1 specific operating system information - i_mode
- 16 bit
- 0~3 (4bits): file format
- 4~6 (3bits)
- u bit: setuid(set user id)
- g bit: setgid(set group id)
- s bit: sticky bit, used when a task is removed from the memory or for a shared directory
- 7~15 (9bits): access control
- 7~9 (3 bits): user access
- 10~12 (3 bits): user group access
- 13~15 (3 bits): other access
- 16 bit
- i_block[15]: used for disk block location management
- 12 direct blocks: pointers indicating disk blocks, max. 48 KB
- 3 indirect blocks: pointers indicating pointers indicating disk blocks
- single indirect block: max. 4 MB
- double indirect block: max. 4 GB
- triple indirect block: max. 4 TB
- i_mode
-
directory entry: connect an inode to a file name
-
FAT directory entry
struct msdos_dir_entry { __u8 name[MSDOS_NAME];/* name and extension */ __u8 attr; /* attribute bits */ __u8 lcase; /* Case for base and extension */ __u8 ctime_cs; /* Creation time, centiseconds (0-199) */ __le16 ctime; /* Creation time */ __le16 cdate; /* Creation date */ __le16 adate; /* Last access date */ __le16 starthi; /* High 16 bits of cluster in FAT32 */ __le16 time,date,start;/* time, date and first cluster */ __le32 size; /* file size (in bytes) */ }; -
ext2 directory entry
#define EXT2_NAME_LEN 255 struct ext2_dir_entry { __le32 inode; /* Inode number */ __le16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */ __le16 name_len; /* Name length */ char name[]; /* File name, up to EXT2_NAME_LEN */ };
-
Ext2 File System
- IDE disks
- /dev/hda, /dev/hdb
- SCSI disks
- /dev/sda, /dev/sdb
-
Partition in Ext2 file system

Advisory Lock vs. Mandatory Lock
-
 Cool Wind on Study
Cool Wind on Study